What Size Hiatal Hernia Needs Surgery
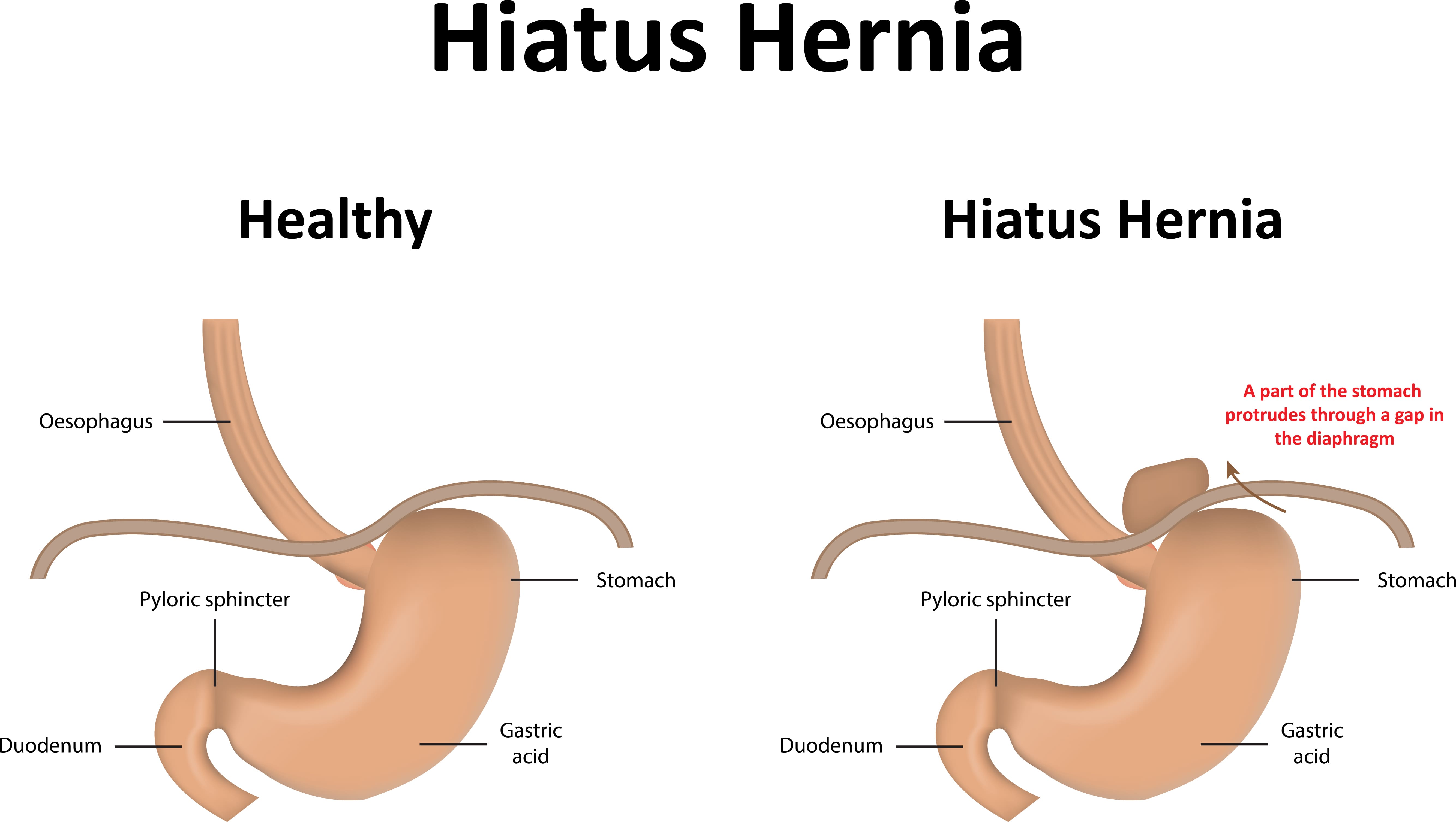
To understand what size hiatal hernia requires surgery, we need to understand what it is. A hiatal hernia refers to an intra-abdominal hernia. It most often occurs when the upper part of the stomach passes through the opening of the diaphragm where the esophagus should pass.
Doctors often use the terms "esophageal reflux" and "hernia of the orifice of the diaphragm" as synonyms. However, this is not entirely correct. In the first case, we are talking about a clinical diagnosis, which is based on the manifestation of symptoms such as heartburn and acid secretion into the esophagus. The diagnosis is confirmed by special tests that assess the degree of gastric juice reflux.
Hernia of the orifice of the diaphragm is a diagnosis of an anatomical change. It is quite difficult to detect it with tests, so a number of procedures are required to determine the diagnosis. For example, endoscopy of the upper abdomen or X-ray examination.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the images will show how the hernia causes the valve mechanism to open, which encourages stomach contents to reflux back into the esophagus. At the same time, many patients complain of pain arising in the upper abdomen. But most hiatal hernias no larger than 2.5 inches are usually pain-free.
If an esophageal hernia of the diaphragm is large and causing pain, surgery may be necessary. Surgery can help prevent a pinched stomach.
Is surgical treatment of a hiatal hernia mandatory?
Most hiatal hernias are not accompanied by painful symptoms and are not dangerous. However, they can develop over time when the opening of the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes enlarges. Usually a hernia is diagnosed at the time when the patient has symptoms of reflux.
Typically, when a hiatal hernia occurs, patients may experience the following signs of the disease:
- chest and abdominal pain;
- difficulty swallowing food;
- bloody stools;
- heartburn and belching;
- a bitter taste in the mouth;
- severe shortness of breath on exertion;
- vomiting blood.
The diaphragm helps the valve between the stomach and esophagus work. People with a hiatal hernia often have reflux because the valve can no longer normally perform its natural functions. If hernias of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm reach a large size, they are commonly called paraesophageal hernias. This diagnosis already threatens serious consequences for the patient and requires surgical intervention, even if the symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves.
What can happen if hiatal hernia is not treated
Most hiatal hernias do not require surgery. However, if the hole in the diaphragm increases in size and grows into a paraesophageal hernia, surgery cannot be avoided. This can lead to torsion of the stomach and possible loss of the organ. In life practice, there are many cases where neglected hernias have caused deaths.
Symptoms of paraesophageal hernias
Paraesophageal hernias are one of the varieties of chiasal hernias, which occur when the size of the diaphragm increases. In such situations, there is a great risk of blockage of the stomach and loss of normal blood supply. At the same time, many patients experience constant chest pain and frequent abdominal bloating. In most cases, surgery will be necessary to prevent the loss of the stomach. In some situations, surgery must be performed in an emergency.
What is the best treatment for hiatal hernia and reflux
To do surgery or not, it is up to the attending physician to decide after all the tests are done. But in some cases, it is the only right decision when a hiatal hernia occurs. Most such hernias do not require surgery. The exception is when the patient has reflux. The surgeon fixes the hernia when performing surgery so that it does not grow beyond its size.
What causes a hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm
In fact, even experienced surgeons cannot reliably answer this question. A hiatal hernia can form due to the following possible causes:
- as a consequence of a chronic illness;
- after the systematic lifting of heavy weights;
- with constant abdominal pressure due to severe coughing or constipation;
- as a result of aging of the body.
Most often hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm is observed in the elderly. This is not surprising, because the tissues of the body with age significantly weaken, just because of this, a small hernia can increase in size and lead to undesirable consequences.
When is surgical treatment of a hiatal hernia necessary?
The large size of a hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm can lead not only to unpleasant pain symptoms, but in some cases even to death. When the hole of the diaphragm exceeds 6 centimeters, the patient's stomach can be in the chest, which of course will bring discomfort when eating and cause pain. At the same time, people often experience bloating in the upper abdomen, early satiation with food, and shortness of breath.
Large hiatal hernias can also cause chronic blood loss, which subsequently threatens anemia. If all symptoms point to a hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm, it is likely that surgery cannot be avoided. In such cases, only surgery can help control the painful symptoms.
Surgery can take place in the usual way or by laparoscopy. In the first case, an incision is made in the upper abdomen and the surgeon gently sews up the extra gap that has appeared in the diaphragm. The esophagus is not affected. After the operation, a suture is applied and appropriate procedures are prescribed for the recovery of the body.
Laparoscopy is a gentler surgical procedure than conventional surgery. The surgeon makes 1-2 small incisions on the abdomen and with the help of special devices, the gap in the diaphragm is sewn up to its normal size. After laparoscopy, you will only need to stay in the hospital for 3-4 days, as the body recovers much faster. In some cases, patients are discharged the day after surgery.
What is better - open surgery or laparoscopy
Surgery is always prescribed by the attending physician depending on the severity of the hernia and the symptoms. The patient's condition determines just what kind of surgery should be prescribed - conventional or laparoscopic surgery. Both situations have their own peculiarities. For example, laparoscopy requires a long general anesthesia, which is contraindicated for some people.
At the same time, such a surgical intervention is less traumatic to the tissues and requires a minimum of time to recover from surgery. For patients who are not allergic to pain medications, laparoscopy is the optimal solution for hernia repair. After it, a person will be able to return to daily life much faster compared to the recovery period after a hollow operation.
Other ways to treat a hiatal hernia
If patients have minor symptoms and the hernia is no more than two centimeters in height, the treating physician may prescribe alternative treatments. For example, fundoplication without the need for tissue incision. This method is quite effective and has fewer side effects on the body. In addition to fundoplication, surgeons prescribe a reflux control system for the treatment of hiatal hernia, which also does not require surgery and shows good results in controlling painful symptoms.
Do you need to follow a special diet for a hiatal hernia
If the hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm is not large and does not cause unpleasant symptoms, no diet will be required. If the size of the hernia is quite large, you should consider having surgery to avoid unpleasant problems in the future. When patients have reflux, foods that can cause allergies or other adverse reactions should be avoided.
Most commonly, such foods include chocolate, tomatoes, citrus fruits, milk, fried foods, etc. It is also not recommended to consume alcoholic beverages during the exacerbation of symptoms and during the recovery period after surgery. Anyway, you should know: food does not aggravate reflux if you do not abuse spicy, salty or fried foods.
Is surgery for hiatal hernia repair dangerous
Any surgical intervention in the body involves certain risks. Such a measure of getting rid of a hernia is prescribed only by the attending physician after collecting all the tests and conducting tomographic studies. In most cases, if the hernia is neglected, laparoscopy is appointed. If necessary, the surgeon additionally prescribes painkillers.
During the recovery period after surgery, patients are not recommended to lift weights. It is also necessary to follow a certain diet. Salty, fried and fatty foods are usually excluded from the daily menu. The minimum period of abstinence is 30 days.
Conclusion
You should not start a hernia of the esophageal orifice of the diaphragm, it can lead to the most dire consequences. If you are concerned about pain in the abdomen and chest area, you have difficulty swallowing food, or you notice blood when defecating - we advise you to see a doctor immediately. Despite the fact that not every case will require surgery, if a hernia is diagnosed, you should not allow it to develop further. So do not delay going to the doctor if you have the first symptoms of malaise.


